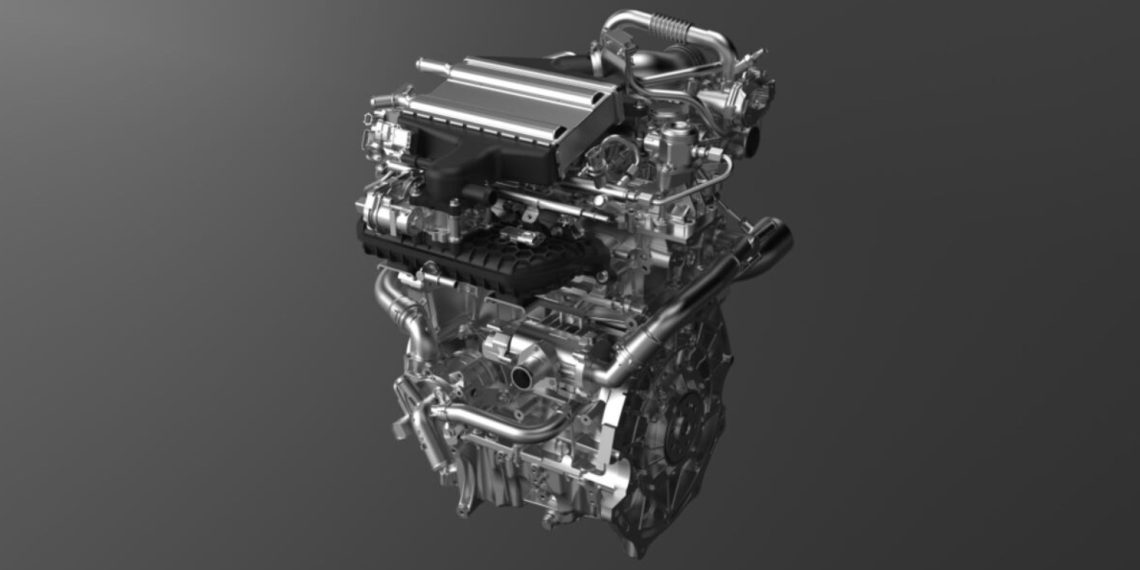
GAC’s (Guangzhou Automobile Group Co., Ltd) achievement in developing an ammonia-powered engine marks a significant milestone in the automotive industry’s quest for more sustainable and eco-friendly energy solutions. While ammonia has long been used as a fertilizer and in various industrial applications, its potential as a fuel for passenger cars is just beginning to be explored.
The Advantages of Ammonia as a Fuel
Ammonia has several advantages that make it an attractive option as an alternative fuel source. First and foremost, it is carbon-free, meaning it does not produce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions when burned. This is a major advantage in the fight against climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, ammonia is abundant and can be produced from renewable sources, further enhancing its appeal as a sustainable fuel option.
Challenges and Solutions
Developing an ammonia-powered engine for passenger cars presented unique challenges that GAC had to overcome. Ammonia has low flammability, which requires careful engineering to ensure efficient combustion. GAC’s engineers were able to design an engine that effectively addresses this challenge, allowing ammonia to be burned in a safe and controlled manner. Furthermore, ammonia combustion tends to produce high levels of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, which are harmful pollutants. GAC’s engine design tackles this issue as well, achieving a significant 90% reduction in carbon emissions compared to traditional combustion engines.
Safety Considerations and Regulatory Compliance
Ammonia, being a toxic substance, necessitates strict safety measures to ensure its safe handling and use in passenger cars. GAC has worked diligently to develop a high-safety architecture that meets the necessary requirements for ammonia-powered vehicles. This includes implementing robust safety protocols and systems to mitigate potential risks associated with ammonia storage and usage.
The Future of Ammonia-Powered Cars
While GAC’s achievement is groundbreaking, the journey towards widespread adoption of ammonia-powered cars is still in its early stages. Several key factors will play a crucial role in determining the feasibility and success of this technology. Regulatory bodies will need to establish clear guidelines and safety standards for ammonia-powered vehicles to ensure public safety. Additionally, the development of a comprehensive and efficient infrastructure to support the production, distribution, and availability of ammonia fuel will be essential.
Collaboration and Industry Support
GAC’s pioneering work in ammonia-powered engines has the potential to inspire collaboration within the automotive industry. Other manufacturers may join forces with GAC to further research and develop ammonia-powered vehicles, leading to shared knowledge and advancements in the field. This collective effort will help accelerate the progress towards sustainable transportation and reduce reliance on traditional fossil fuels.
As GAC continues to refine and improve its ammonia-powered engine technology, the future looks promising for ammonia as a viable fuel option for passenger cars. With its commitment to green energy transition and innovation, GAC is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of sustainable mobility. The successful integration of ammonia-powered cars into the market will bring us closer to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation ecosystem.