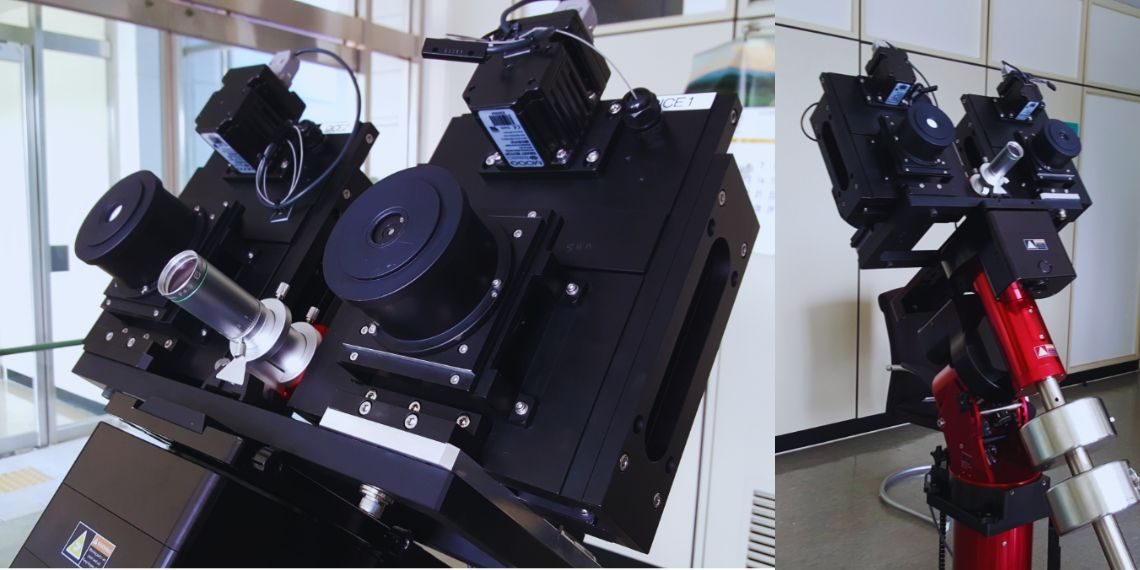
South Korea’s space agency, KASA, has teamed up with NASA to launch a groundbreaking solar observation instrument, the CODEX solar coronagraph, to the International Space Station (ISS). Designed to capture unprecedented data on the Sun’s corona and the solar wind, this mission symbolizes a deepening partnership between the two nations in the field of space exploration. The CODEX instrument is set for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy Space Center, Florida.

Key Points
KASA and NASA collaborated to launch the CODEX solar coronagraph on the ISS mission.
CODEX will capture critical data on the Sun’s corona, solar wind temperature, velocity, and density.
The launch is scheduled from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, aboard SpaceX’s Falcon 9.
CODEX will enhance solar weather forecasts and provide insights into solar phenomena.
South Korea becomes the fifth nation to collaborate with NASA on the Artemis lunar program.
CODEX Solar Coronagraph Mission: A Collaborative Milestone
The CODEX (Coronal Diagnostic Experiment) solar coronagraph represents an advanced scientific instrument co-developed by KASA and NASA to study the solar corona and solar wind. Once attached to the ISS, CODEX will spend approximately 55 minutes observing the Sun during each orbit of the Earth. By capturing data on solar wind temperature, velocity, and density, CODEX aims to improve our understanding of the Sun’s atmospheric dynamics, potentially enabling better predictions of space weather that impact satellites and other space technology.
Expanding International Space Partnerships
This collaboration between KASA and NASA reflects an expanding partnership. Alongside CODEX, South Korea and the United States are working together on NASA’s Artemis lunar exploration program, with KASA participating in sustainability-focused lunar research and Mars mission feasibility studies. By joining the Artemis initiative, South Korea underscores its commitment to deep-space exploration and advances as a key player in global space missions. This cooperation builds on previous bilateral agreements, making South Korea the fifth country to join NASA’s efforts for sustainable lunar and interplanetary exploration.
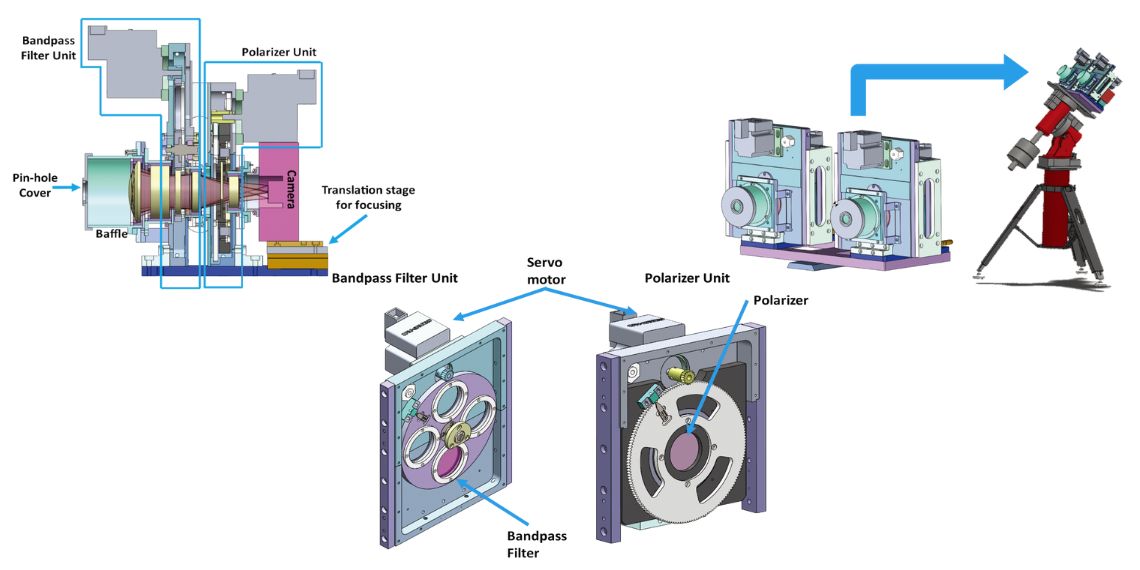
Future-Oriented Studies and Advanced Technology
The joint efforts of KASA and NASA span beyond the CODEX mission, incorporating a wide range of exploratory goals. The two agencies will conduct feasibility studies on lunar landers, work on navigation systems, and enhance astronaut support technology. Additional projects focus on lunar surface science, autonomous power, and robotic operations, with a particular emphasis on cis-lunar space operations (the area between Earth and the Moon). This extensive collaboration is anticipated to advance technological innovations that will drive the next wave of exploration and help establish a sustained human presence on the Moon.
Conclusion
The CODEX solar coronagraph mission represents more than a scientific leap; it is a testament to the power of international collaboration in tackling complex space challenges. As KASA and NASA partner on ambitious projects, from observing the Sun’s corona to exploring the Moon and beyond, their combined efforts may yield transformative insights, shaping the future of space exploration and providing essential data to protect space-based technologies.
Follow Before You Take on Facebook | Twitter | WhatsApp Channel | Instagram | Telegram | Threads | LinkedIn, For the Latest Technology News & Updates | Latest Electric Vehicles News | Electronics News | Mobiles News | Software Updates