The global landscape has been dramatically reshaped by the COVID-19 pandemic, triggering significant shifts in various aspects of our lives. While the pandemic’s immediate impact has subsided, its enduring influence on our behaviors and routines remains evident. Working from home, for instance, has transitioned from being a rarity to a norm. Such transformations have not only impacted individuals but also corporations and industries, prompting adaptations to new realities.
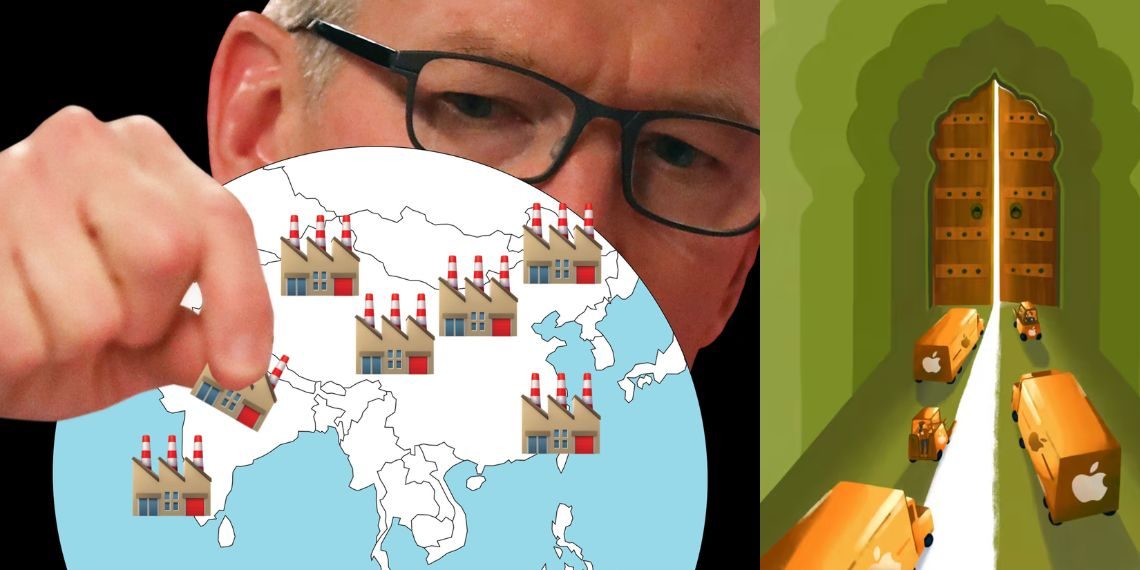
China, where the pandemic originated, faced disruptions across various sectors, including manufacturing. This led numerous companies to rethink their supply chain strategies and explore alternatives to mitigate future risks. Apple, a tech giant reliant on China for significant production, embarked on a journey to diversify its manufacturing base. One of its strategic destinations was India, and recent reports suggest that Apple’s ambitions in the country are set to grow further.
Apple’s Expansion Plans in India
Apple has been actively investing in India to expand its manufacturing capabilities and reduce dependency on China. Reports indicate that the company is now aiming to intensify its efforts by increasing domestic component manufacturing in India. In a meeting with top officials from India’s finance ministry, Apple expressed its intentions to enhance its local component base, underscoring its commitment to the Indian market.
The discussions during the meeting revolved around understanding the supply chain dynamics and the potential to indigenize more manufacturing processes. While the government might not offer specific tax incentives to Apple, the company remains steadfast in its pursuit of investing in India. The goal is to accelerate the process of localization and augment the domestic component manufacturing ecosystem.
Strategic Diversification Beyond China
Apple’s inclination to bolster domestic component manufacturing in India aligns with its broader strategy of diversifying its supply chains away from heavy reliance on China. A significant portion of Apple’s suppliers is concentrated in China, prompting the company to explore ways to distribute its manufacturing capabilities across various regions. India, with its large and skilled workforce, favorable policies, and growing electronics industry, emerged as a viable choice for Apple’s expansion plans.
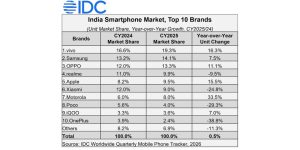
Apple’s association with India’s manufacturing landscape dates back to 2017 when it started assembling iPhones locally. Presently, about 7% of iPhones are manufactured in India, and this proportion is poised to increase in the foreseeable future. Apple’s intentions not only indicate its commitment to the “Make in India” initiative but also its aim to contribute to the growth of India’s electronics manufacturing sector.
Boosting India’s Electronics Industry
Apple’s decision to enhance domestic component manufacturing in India carries substantial implications for the country’s electronics industry. India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme has already garnered considerable interest from smartphone manufacturers, attracting investments and job opportunities. Apple’s move is anticipated to amplify this trend further.
The anticipated surge in manufacturing activities is expected to generate employment, stimulate economic growth, and enhance self-reliance in electronics manufacturing. India’s aspirations of becoming a global electronics manufacturing hub are bolstered by Apple’s commitment to expanding its footprint in the country.
In essence, Apple’s strategic decision aligns with both its business interests and India’s economic goals. As the global tech landscape evolves, partnerships between tech giants and emerging economies like India pave the way for a mutually beneficial future.