Japan is on the brink of revolutionizing its electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, with plans to accelerate its charging capabilities by the end of the decade. Insights from Nikkei reveal that Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) is preparing to take significant strides in enhancing its fast-charging infrastructure, positioning the nation for an electrified future.
Current EV Charging Landscape in Japan
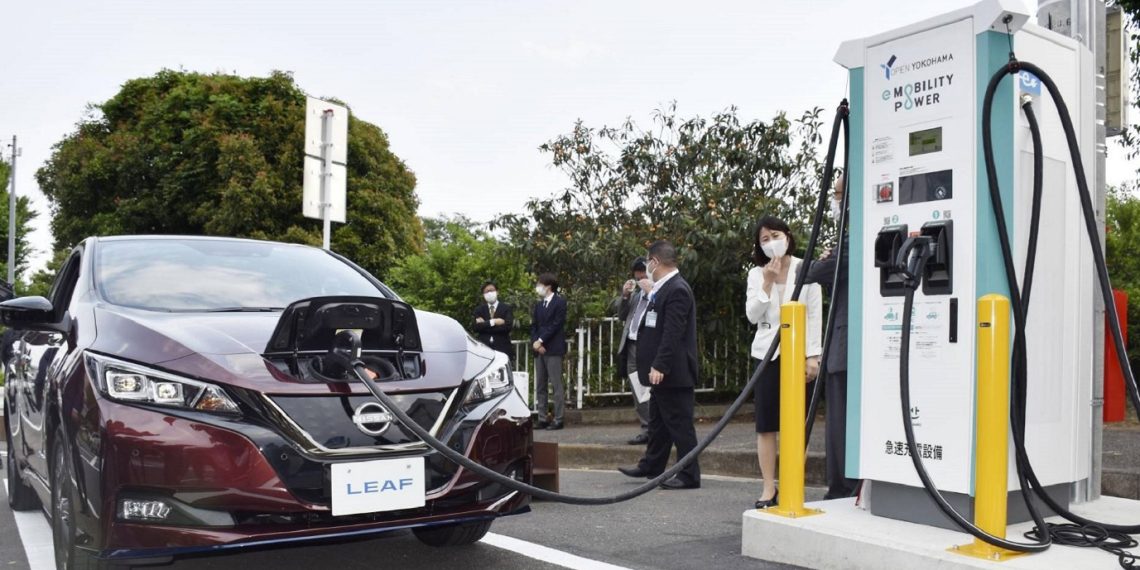
Japan’s EV charging infrastructure has lagged behind that of Europe and the United States. One key factor contributing to this disparity is the existing charging power at highway stations. Presently, the standard charging power averages around 40 kW. However, METI aims to transform this scenario by raising the charging power to 90 kW by the year 2030.
Unveiling METI’s Plans
METI’s strategy focuses on improving the charging power at highway stations, aiming to provide faster and more efficient charging options for EV users. The push for 90 kW charging is a significant improvement from the current situation, which is a consequence of the widespread installation of 50 kW CHAdeMO chargers during the early phases of electric mobility. While these chargers were numerous, their charging speed remained limited.
Comparison with Global Standards
Despite the proposed increase, the 90 kW charging benchmark still falls short when compared to global standards. In contrast to Europe and the US, where charging stations can offer an impressive 250-350 kW, especially along major highways, Japan’s goal might be deemed conservative for the evolving landscape of electric vehicles.
Denser Charger Placement and Subsidies
METI’s plans extend beyond power enhancement. The initiative also involves placing chargers more densely, with one charger approximately every 44 miles along highways. This move is incentivized by subsidies provided to charging station operators. This strategy aims to make charging infrastructure more accessible and user-friendly.
Transitioning to Transparent Pricing
Another notable aspect of METI’s strategy is the shift from time-based to energy-specific pricing. The plan is to implement a pay-per-kWh system, offering users a transparent and fair method of payment. This transition, set to be in place by around 2025, could play a pivotal role in encouraging more EV adoption by offering clarity and convenience in charging costs.
Aligning with the Global Electrification Drive
METI’s efforts are aligned with the global movement towards electrification. However, the cautious approach toward power enhancement serves as a reminder that substantial progress requires careful planning and resource allocation. To truly embrace the spirit of the EV revolution, Japan may need to lay out comprehensive plans that address power limitations and the steps necessary to achieve ambitious goals.