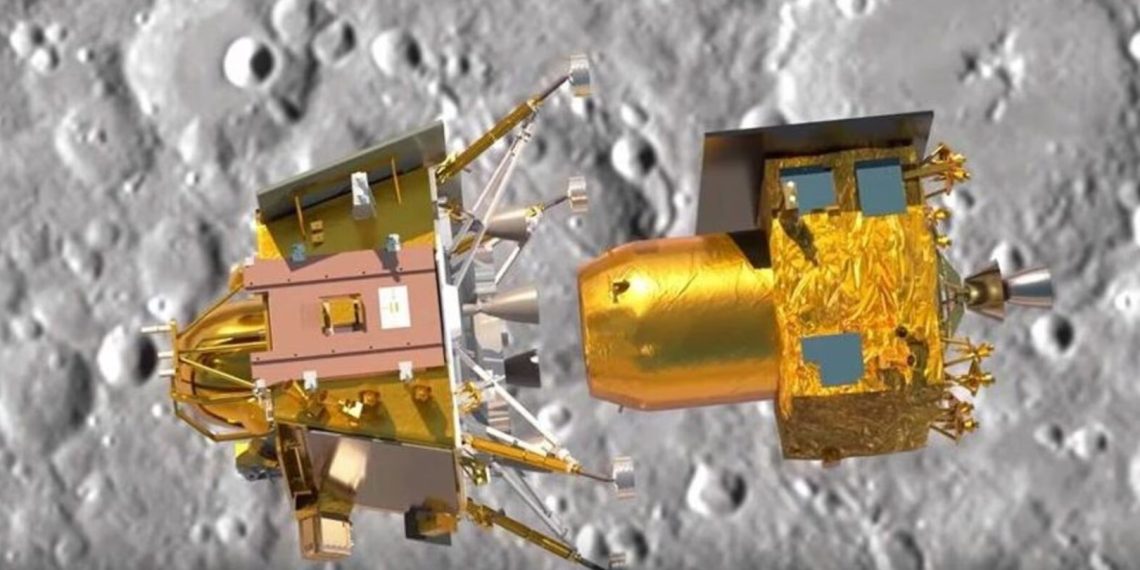
India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission has embarked on a historic journey, aiming to achieve a soft landing on the Moon’s South Pole, marking a significant milestone for ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation). This daring endeavor comes with a budget of Rs 615 crore, approximately $75 million. In this article, we delve into a comparative analysis of Chandrayaan-3’s budget in relation to other notable lunar missions conducted by global space agencies, including China, Russia, and India’s past missions.
A Historic Leap for India
Should the Chandrayaan-3 mission succeed in its objective, India will etch its name as the fourth nation to achieve a lunar landing, joining the ranks of the United States, Soviet Union, and China. Importantly, India’s achievement would be unique as it would mark the first-ever landing on the Moon’s South Pole.
Budget Breakdown: Chandrayaan-3 vs. Chandrayaan-2 and Chandrayaan-1
ISRO’s budget allocation for Chandrayaan-3 at Rs 615 crore is a notable achievement, considering the mission’s ambitious objective. This cost-effective approach contrasts with the budget of Chandrayaan-2, which aimed for a similar lunar landing and had a higher budget of Rs 978 crore. Chandrayaan-1, India’s inaugural lunar mission launched in 2008, took to the skies with a budget of around Rs 386 crore.
Russian Luna25 Mission: A Costly Endeavor
While the Russian government has not officially disclosed the budget for the Luna25 mission, which encountered a crash landing on the Moon’s surface, estimates suggest that the project could have cost anywhere between Rs 1,000 to Rs 1,600 crore. This stark contrast in budget magnitudes emphasizes ISRO’s adeptness at achieving significant milestones while managing costs effectively.
China’s Chang’e 4: Lunar Success on a Budget
China’s Chang’e 4 mission achieved a successful soft landing on the Moon’s far side in January 2019. What’s intriguing is the reported budget, which is roughly equivalent to the cost of constructing about one kilometer of subway in China. This budget ranged from 500 million yuan (approximately US$72 million) to 1.2 billion yuan (approximately US$172 million), depending on the region. The comparison underscores ISRO’s cost-efficient approach to space exploration.
Chandrayaan-3’s Countdown to Success
The Chandrayaan-3 mission initiated its journey on July 14 with the Launch Vehicle Mark-III (LVM-3) rocket. Over the course of 41 days, it aims to reach the Moon’s South Pole and execute a successful soft landing. The anticipated moment of truth is scheduled for August 23 at 6:04 PM, when the Vikram Lander Module will attempt a gentle touchdown on the Moon’s surface.
In Conclusion: A Testament to ISRO’s Excellence
As India and the world await the outcome of the Chandrayaan-3 mission, the focus remains on ISRO’s remarkable achievements. The cost-effective approach taken by ISRO to realize ambitious lunar missions showcases the organization’s dedication to advancing space exploration while optimizing resources. Chandrayaan-3’s budget stands as a testament to ISRO’s commitment to expanding human knowledge and leaving an indelible mark in the realm of space exploration.