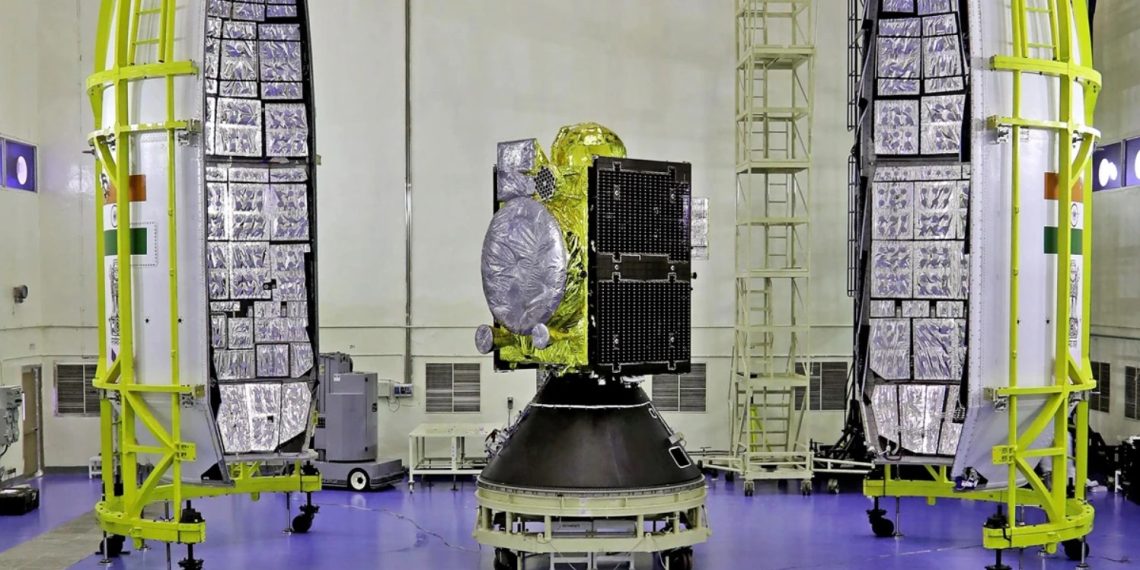
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) achieved another remarkable feat as it successfully launched a navigation satellite, NVS-01, aboard the GSLV-F12 rocket from Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. Following a flawless ascent, the rocket deployed the satellite into a geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO) at an altitude of approximately 251 km. The GSLV-F12, India’s larger rocket, played a crucial role in this mission and expands the country’s capabilities for future space endeavors.
Enhanced Payload Capability and Ambitious Missions
With the successful launch of GSLV-F12, ISRO now possesses the capability to launch even larger payloads, marking a significant milestone for the space agency. The rocket carried the NVS-01 satellite, which represents the first of a new generation of communication satellites. These satellites will form an indigenous constellation, providing India with its own navigation system akin to the widely used Global Positioning System (GPS). The primary objective of this initiative is to enable users to obtain precise location data, crucial for diverse applications such as map services, regional navigation, and missile positioning.
Continuity of NavIC Services and Advanced Capabilities
This launch holds immense importance as it ensures the continuity of NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) services. NavIC is an indigenous regional satellite navigation system designed by ISRO to meet the positioning, navigation, and timing requirements of India. Similar to GPS, it delivers accurate and real-time navigation within India and an extended region of 1,500 km around the mainland. NavIC offers impressive user position accuracy of better than 20 meters and timing accuracy of better than 50 nanoseconds.
Applications and Services of NavIC
NavIC finds extensive use across various sectors, including terrestrial, aerial, and maritime navigation, precision agriculture, location-based services on mobile devices, and marine fisheries, among many others. With its constellation of seven satellites and a network of ground stations operating round the clock, NavIC provides two services: the Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and the Restricted Service for strategic users. Notably, NavIC SPS signals are interoperable with signals from other global navigation satellite systems such as GPS, Glonass, Galileo, and BeiDou.
Impressive Mission Accomplishments and Future Endeavors
The GSLV-F12 mission represents the sixth operational flight of the GSLV with an indigenous cryogenic stage, further highlighting ISRO’s growing expertise in advanced rocket technologies. The NVS-01 satellite is expected to have a mission life of over 12 years, solidifying India’s commitment to long-term space exploration and satellite-based services.
ISRO’s impressive achievements this year span various missions, including crucial tests for the upcoming Gaganyaan human space mission and the highly anticipated Chandrayaan 3 mission, which aims to land a spacecraft on the lunar surface. These endeavors reaffirm India’s position as a prominent player in the global space industry and pave the way for further advancements in space research and technology.