NASA has revealed a groundbreaking prototype telescope designed for the LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) mission, which aims to detect gravitational waves from cosmic events. This collaborative initiative with the European Space Agency (ESA) promises to enhance our understanding of the universe by observing phenomena such as black hole collisions.
Key Points
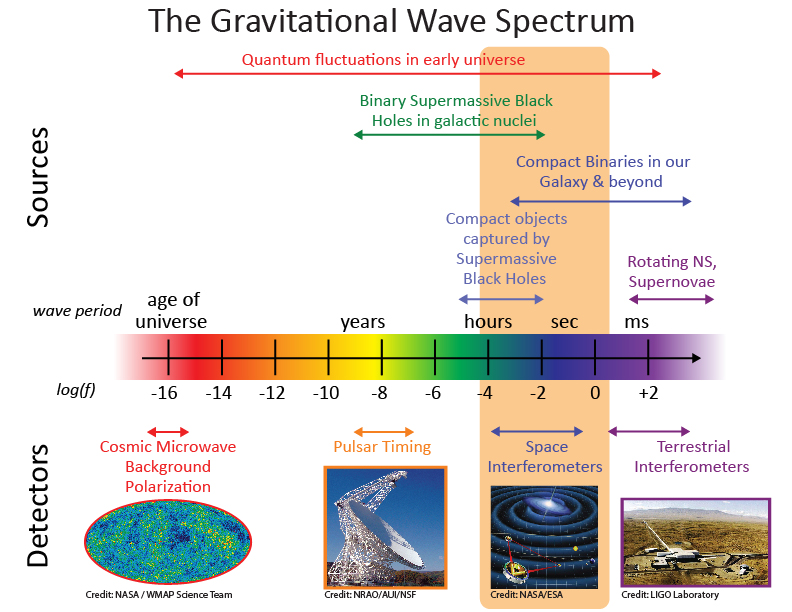
LISA Mission Overview: A joint effort by NASA and ESA to detect gravitational waves through a constellation of three spacecraft arranged in a triangular formation, each spanning approximately 1.6 million miles.
Prototype Telescope Significance: The Engineering Development Unit Telescope is essential for validating the design and construction of the final six telescopes required for the mission.
Advanced Materials: The prototype is made from Zerodur, a stable glass ceramic that maintains precision across varying temperatures. Its primary mirror features a gold coating to enhance infrared reflectivity.
Launch Timeline: The LISA mission is anticipated to launch in the mid-2030s, marking a significant step forward in gravitational wave astronomy.
Future Insights: The mission aims to unlock new knowledge about the universe, including insights into black holes, neutron stars, and the nature of dark matter.

LISA Mission and Telescope Design
The LISA mission represents a pivotal advancement in gravitational wave detection. It employs three spacecraft that form a triangular array, enabling the detection of minute fluctuations in distance caused by gravitational waves. The spacecraft will communicate via infrared laser beams, which are essential for accurate measurements.
NASA is responsible for providing six telescopes for the mission, with the prototype serving as a crucial reference point. This telescope is designed to ensure that the final flight hardware meets the mission’s stringent requirements.

Prototype Telescope Inspection and Materials
The prototype telescope, built by L3Harris Technologies, has undergone rigorous testing at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center since its arrival in May. The use of Zerodur ensures exceptional thermal stability, allowing for precise measurements of gravitational waves. The primary mirror’s gold coating enhances its ability to reflect infrared lasers while minimizing heat loss, making it suitable for the cold vacuum of space.
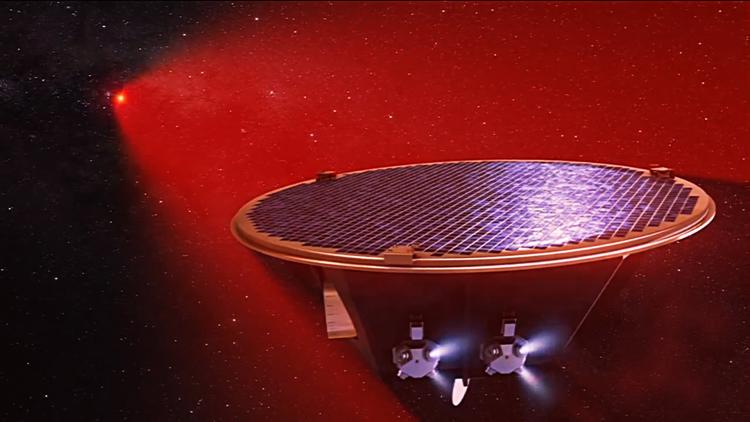

Launch Timeline and Future Prospects
Set to launch in the mid-2030s, the LISA mission is expected to revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos. Successfully detecting gravitational waves, will provide new insights into black hole dynamics and the enigmatic forces of dark energy and dark matter.
Conclusion
NASA’s unveiling of the LISA prototype telescope is a significant milestone in gravitational wave detection. This mission, in collaboration with ESA, will deepen our understanding of the universe and the fundamental forces that shape it. As we approach the anticipated launch in the mid-2030s, the scientific community eagerly awaits the insights that LISA will provide, opening up new avenues for exploration and discovery in astrophysics.
Follow Before You Take on Facebook | Twitter | WhatsApp Channel | Instagram | Telegram | Threads | LinkedIn, For the Latest Technology News & Updates | Latest Electric Vehicles News | Electronics News | Mobiles News | Software Updates